Near Da Nang, South Vietnam, Marines move through ankle-deep mud carry their poncho-covered comrade towards higher ground were, when the weather permits, he will be air-lifted to the rear areas, Jan. 16, 1968. (AP Photo/John T. Wheeler)
South Paris, Maine
Popular struggle for national independence under socialism has regularly provoked U.S. war or hostile interventions, as with Cuba, North Korea, China, Vietnam and other nations. We explore both the extreme danger of possible U.S. war with China and also the changing U.S rationale for fighting wars. This shows in the difference between why the U.S. war in Vietnam was fought and why U.S. war with China may be on the way.
Vietnam recently commemorated agreements reached 70 years ago in Geneva that on July 21, 1954 ended war between Vietnamese revolutionary forces and the French military, defeated two months earlier at Dien Bien Phu. According to official media, the object of a “scientific conference” held on July 19 was “to emphasize the historical importance of the agreements for the struggle for national liberation of the Vietnamese people and the peoples of the world.”

Also on July 19, Nguyen Phu Trong died. Once chairperson of the National Assembly and president of Vietnam, this paramount leader, a student and teacher of Marxist theory, had long served as general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam. His death is a reminder, if such is needed, that for Vietnam revolutionary socialism and national liberation were kindred struggles.
To prevent the unification of Vietnam as a socialist nation, the U.S. government went the last mile, first diplomatically and then militarily – from the 1954 Geneva agreements that established Vietnam’s national independence to the departure of defeated U.S. troops on April 30, 1975. The U.S. leadership class, involved in spreading U.S. power and influence across the globe, created and then defended South Vietnam, while attempting to defeat Vietnam’s Revolution, all at enormous human and material cost.
The enclave remaining after a U.S. victory might have ended up as a beachhead for counter-revolution and U.S. control in Southeast Asia. In their various situations, that’s the role performed by South Korea, Taiwan, and even Ukraine in relation to Russia, and Israel vis-a-vis the rest of the Middle East.
U.S. planners, in thinking about what to do about Vietnam, were not entirely devoid of reason. For U.S. imperialists, to beat back Vietnamese Communists – think “domino theory” – and heat up the Cold War against the Soviet Union had a certain logic, according to their own lights.
After the Vietnam disaster, official U.S. planning for war has built upon a variety of ostensible reasons for fighting. Having emerged from World War II well-resourced and strong, the U.S. government consistently demonstrated limited tolerance for the risings of oppressed, colonialized peoples. However, once newly formed independent states showed signs of strength, regional prominence, or even strategic rivalry, U.S. strategists turned to action.
War materialized as the ultimate U.S. fix, no matter the circumstances and under a variety of pretexts, as shown with U.S. war-making in Libya, Afghanistan, and Iraq. The rationales for fighting were more diffuse. The threat of U.S. war now looms over Iran and, more ominously, over China. Each is under the gun because they are strong, assertive states.
Anti-communism was a safer kind of rationale. Vietnam won its “American War,” and the U.S. government backed off. That’s the story. Incidentally, the Vietnamese people scored a clear win. They live according to plans and socialist purpose in a free and independent nation.
Vietnam has established diplomatic relations with 190 countries. A Vietnamese writer cites “important achievements with infrastructure gradually meeting the needs of industrialization and modernization.” Since reforms in the 1980s, an economy resting mainly on foreign direct investment in manufacturing and tourism has expanded. Economic growth ranged between 9.5 and 5.5 percent between 1993 and 2022, save for sharp drops in 2020 and 2021. GDP rose 5.05 percent in 2023. By 2022, the poverty rate was down to 4.3%.
Vietnam’s government since 2008 has spent 20 percent of its budget on education. The same report mentions “high primary school completion rates, strong gender parity, low student/teacher ratios,” and school attendance rates that are high. The British medical journal Lancet indicates that, “Along with the economic growth, the health of the Vietnamese people has significantly improved between 1990 and 2020, whereby the life expectancy grew from 69 to 75 years, and the under-five child mortality rate decreased from 30 to 21 per 1000 live births.”

Socialist China restored dignity to the vast majority of its citizens, has afforded them decent lives, and created a well-functioning state that responds effectively to the climate crisis and other challenges. It too warrants a pass from the U.S. government.
That’s not happening: the U.S. government, in the hands of a divided leadership class, deals only haphazardly with major problems afflicting U.S. society. It satisfies the material wants of the upper echelons, and presides over war preparations as part of what is, in effect, a new Cold War.
Indeed, the USA has accumulated over 750 bases in 80 countries and posted 173,000 troops in 159 counties. The U.S. share of global arms exports in 2019-23 was 42 percent, up from 34 percent during the previous four-year period, according to sipri.org.
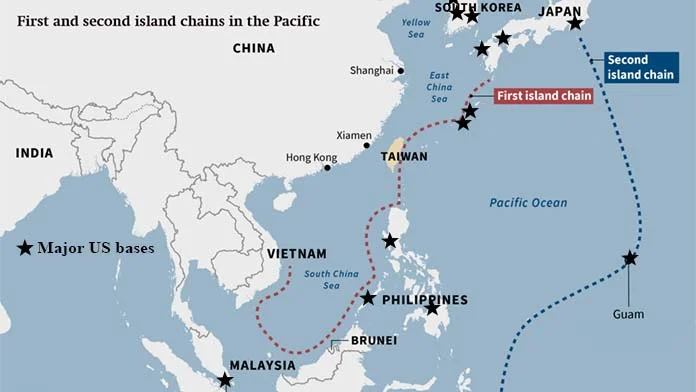
In the Pacific waters surrounding China, the United States has expanded the capabilities of its bases; it operates nuclear-equipped naval vessels, arranges for multi-national naval exercises, has vessels engaging in provocative “freedom of navigation exercises,” and will be introducing nuclear-powered submarines.
The idea of multiple and varied reasons for fighting wars, presented above, folds neatly into the overarching notion of a new Cold War, something that by nature is ambitious, far-reaching, and long term. Where is the justification for that?
Here is a guess: The United States decades ago turned to a great variety of activities related to military preparation, financing, and recovery. These now intrude massively in the U.S. economy and in society itself, so much so that, in theory, something has to happen to explain and justify such a state of affairs. War provides meaning, without which the whole apparatus might disappear. What then of the economy and of the collective experience of a U.S population variously oriented to the military?
The Costs of War Project of the Watson Institute of Brown University weighs in. Author Heidi Peltier points out that:
Federal spending on the military and on veterans makes up more than half of the federal discretionary budget. Employment in the federal government is dominated by civilian defense workers and uniformed military personnel. Because the majority of taxpayer dollars and federal resources are devoted to the military and military industries, and most government jobs are in the defense sector, the political power of this sector has become more deeply entrenched and other alternatives have become harder to pursue. Instead of having a federal government that addresses various national priorities … the U.S. has a government that is largely devoted to war and militarism.

Unfortunately, protecting both the U.S. economy and habituation to the military has its downside, specifically extreme danger to humanity itself. Writing in the most recent issue of Monthly Review magazine, John Bellamy Foster and Brett Clark explain, pointing to China. Discussing “Imperialism in the Indo-Pacific,” they state that:
“Most U.S. strategies for winning the New Cold War directed at China are aimed at a strategic-geopolitical defeat of the latter that would bring down Chinese President Xi Jinping and destroy the enormous prestige of the Communist Party of China, leading to regime change from within and the subordination of China to the U.S. imperium from without … (It) is the United States, which sees China’s rise as a threat to its own global preeminence, with the Indo-Pacific super-region increasingly being viewed as the pivotal site in the New Cold War, that is propelling all of humanity toward a Third World War.”
W.T. Whitney Jr. is a political journalist whose focus is on Latin America, health care, and anti-racism. A Cuba solidarity activist, he formerly worked as a pediatrician, lives in rural Maine. W.T. Whitney Jr. es un periodista político cuyo enfoque está en América Latina, la atención médica y el antirracismo. Activista solidario con Cuba, anteriormente trabajó como pediatra, vive en la zona rural de Maine.